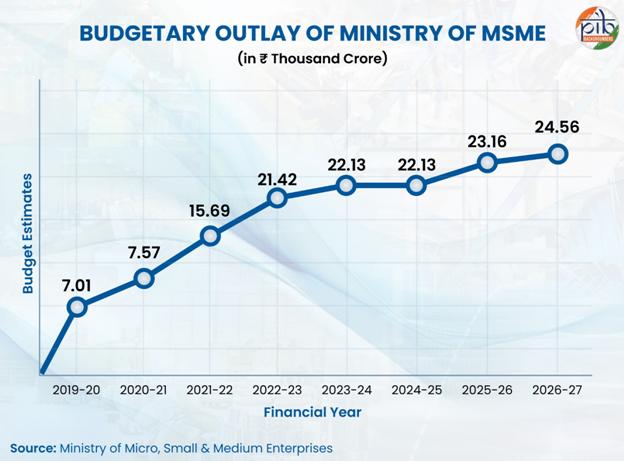
New Delhi, Delhi, 15th of February, 2026 : The Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises envisions a vibrant MSME sector by promoting its growth and development. It primarily supports states in promoting entrepreneurship, generating employment and livelihood opportunities, and strengthening the competitiveness of MSMEs. Over the years, the Budget outlay for the Ministry has been on a consistent rise, focusing on the long-term goal to enhance the performance of MSMEs through skill and entrepreneurship development.
The Union Budget 2026–27 introduces multiple measures to strengthen the MSME sector by enhancing financial support, promoting innovation, and easing regulatory compliance. Through these initiatives, the Government aims to improve the competitiveness of MSMEs in both domestic and global markets.
Three-pronged approach to help MSMEs grow as Champions under first Kartavya
Equity Support: Under equity support measures, a dedicated ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund has been announced to generate future champions by incentivizing enterprises based on defined eligibility criteria. In addition, the Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund, established in 2021, will be increased with ₹2,000 crore to sustain support for micro enterprises and ensure continued access to risk capital. Notably, the SRI Fund has assisted 682 MSMEs by way of investment worth ₹15,442 crore (as of 30 November 2025).
Liquidity Support: On this front, ₹7 lakh+ crore has already been unlocked for MSMEs through the TReDS platform. To fully harness its potential, four key measures have been announced–
-
- Mandate TReDS as the settlement platform for all purchases from MSMEs by CPSEs, setting a benchmark for other corporates.
- Introduce CGTMSE-backed credit guarantee support for invoice discounting on TReDS platform.
- Integrate GeM with TReDS to enable information-sharing with financiers on government MSME purchases, facilitating faster and cheaper credit.
- Understanding TReDSTReDS is an electronic platform facilitating financing, discounting of trade receivables of MSMEs via multiple financiers. The receivables can be due from corporates, other buyers, incl. Government Departments, PSUs. Introduce TReDS receivables as asset-backed securities to deepen the secondary market, improve liquidity, and speed up settlements.

Professional support: As per the final approach, the Government will facilitate Professional Institutions such as ICAI, ICSI, ICMAI to design short-term, modular courses and practical tools to develop a cadre of ‘Corporate Mitras’, especially in Tier-II and Tier-III towns. These accredited para-professionals will help MSMEs meet compliance requirements at affordable costs.
Tax proposal to unlock global markets for India’s small businesses
The Budget proposes to remove the existing ₹10 lakh limit per consignment on courier exports, which is likely to reduce friction in cross-border B2C trade. This will help India’s small businesses, artisans, and start-ups reach global markets through e-commerce. It also aims to improve the handling of rejected and returned shipments by using technology to better track and identify such consignments.
Powering MSMEs: Policies Turning Potential into Performance
| Udyam Registration Portal was launched in 2020 to enable ease of registration for MSMEs and have access to all schemes and benefits. The registration process remains free of cost, paperless and digital. Further, the Udyam Assist Platform (UAP) Portal on was launched in January 2023, for bringing Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs) into the formal ambit, and for availing Priority Sector Lending (PSL) benefits. |
The MSME sector witnessed a digital transformation milestone in 2025 with formalization on the rise. Over 7.30 crore enterprises have been registered on Udyam Registration Portal and Udyam Assist Platform, from 1 July 2020 to December 2025. This includes 4.37 registrations on the Udyam Portal and 2.92 crore on the Udyam Assist Platform.

The Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
PMEGP supports micro-entrepreneurs by offering margin money subsidies on bank loans. It has been expanded to include higher project costs and an enhanced scope of activities. Since inception (FY 2008-09), till FY 2025-26 (December 2025), 10.71 lakh+ micro enterprises have been assisted with disbursement of Margin Money subsidy of ₹29,249.43 crore, generating a total estimated employment for 87 lakh+ persons.
MSME Champions Scheme
The MSME Champions Scheme aims to identify and nurture select enterprises by upgrading their processes, minimizing inefficiencies, improving competitiveness, and supporting their growth to achieve excellence in both domestic and international markets.
It has three components- ‘MSME-Sustainable (ZED)’, ‘MSME Competitive (LEAN)’ and ‘MSME-Innovative (Incubation, Design & IPR). To bolster competitiveness, the MSME Champions Scheme promotes “Zero Defect, Zero Effect” practices through ZED Certification and productivity improvements via the MSME Competitive (Lean) Scheme. Innovation is also being institutionalized via the MSME-Innovative component, which enables incubation, design interventions, and protection of IPR (Intellectual Property Rights).
| A total of 2,71,373 MSMEs registered under MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification Scheme & 1,92,689 enterprises were certified. A total of 32,077 MSMEs registered under MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme and 31,987 MSMEs took the Lean pledge, a “pre-commitment” to uphold values of Lean Practices & Philosophy. |
Initiatives for promoting e-commerce and supply chains
The rapid expansion of the ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce) ecosystem, along with the TEAM (Trade Enablement and Marketing) Initiative- which targets onboarding 5 lakh MSMEs-provides a transformative pathway for MSMEs to integrate into formal e-commerce and supply chains while significantly lowering transaction costs.
Online Dispute Resolution (ODR)
| DID YOU KNOW? ODR portal was launched on 27 June 2025- MSME Day. |
The MSE Scheme for Online Dispute Resolution (ODR) on delayed payments, together with the MSME ODR Portal developed under it, establishes a structured, pre-adjudication framework that promotes amicable, dialogue-based settlements between buyers and sellers before proceedings under the MSMED Act, 2006. This mechanism enables MSMEs to recover dues efficiently while preserving ongoing business relationships.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGSMSE)
A Credit Accessibility Breakthrough, the CGSME provides credit guarantees for credit facilities extended by Member Lending Institutions to MSEs without collateral security or third-party guarantees.
- It celebrated 25 years in 2025 wherein it crossed 1 crore guarantees since its inception (August 2000).
- 29.03 lakh guarantees have been approved worth ₹3.77 lakh crore (1 January to 30 November, 2025).
- The ceiling of guarantee coverage has been enhanced to ₹10 crore from ₹5 crore.
- A special provision for MSEs promoted by transgender entrepreneurs has been introduced, providing a 10% concession in guarantee fees and enhanced guarantee coverage of 85% (effective 1March 2025).
PM Vishwakarma Scheme
Launched in September 2023, Vishwakarma Scheme provides end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople of 18 trades who work with their hands and tools.
- Under the scheme, 20 lakh+ artisans are being imparted training and banking support, and 7.7 lakh beneficiaries completed basic skill training in 2025 alone.
- As of 1 December 2025, 30 lakh beneficiaries have been registered, out of which 23.09 lakh beneficiaries have been trained.
- In 2025, ₹2,257 crore was sanctioned to 2.62 lakh beneficiaries in the form of collateral-free loans and 6.7 lakh beneficiaries are digitally enabled.
- DID YOU KNOW?30,000+ Vishwakarma beneficiaries have been onboarded on the Government e-Marketplace, increasing their access to institutional buyers. Online marketing support is being provided to PM Vishwakarma beneficiaries via e-commerce platforms to promote the sale of their products in the domestic and international markets.
Labour reforms
The Labour Codes aim to modernise India’s labour ecosystem by formalising employment, simplifying compliance through digitisation, strengthening social security, and ensuring workplace safety and equity. By rationalising thresholds, streamlining procedures, reducing inspections, and enabling predictable timelines, the reforms ease long-standing compliance burdens on MSMEs while creating a balanced framework that supports enterprise growth and safeguards worker welfare.
Conclusion
Over the decades, the MSME sector has evolved into one of the most vibrant pillars of the Indian economy. By generating large-scale employment at relatively low capital cost, fostering industrialization in rural and backward regions, and supporting balanced regional development, MSMEs have contributed significantly to equitable growth and socio-economic progress. As vital ancillary partners to large industries, they strengthen the broader industrial ecosystem
Today, MSMEs stand at the heart of India’s development trajectory. With their scale, diversity, and resilience, they are well-equipped to harness the ongoing manufacturing momentum and deepen India’s integration into global value chains, transitioning towards more formal, innovation-driven, and export-oriented growth.










More Stories
Consortium-Driven Innovation Model Pioneered By IIT Madras Enables Immediate And Appropriate Technology Commercialisation: Dr. Jitendra Singh.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi Greets Everyone On Mahashivratri.
Consumer Rights Outreach Deepens As New Capacity-Building Series For Gram Panchayats Is Launched.